What is CMM? Types of CMM and Probs
Dec 13, 2025
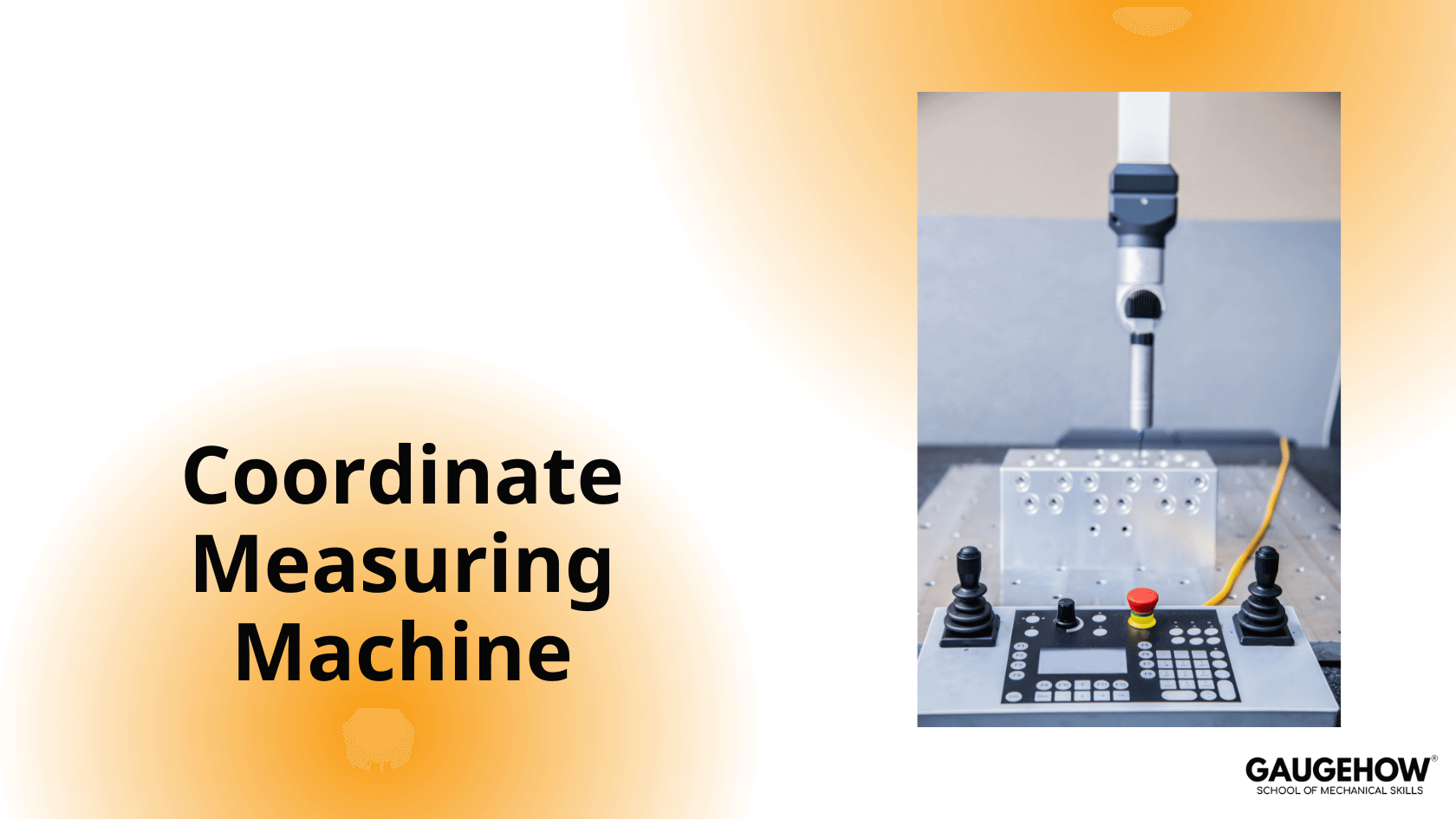
A CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) is a precision measuring machine used to check the size, shape, and position of parts.
It works by touching (or scanning) a component with a probe and recording the exact X, Y, and Z coordinates of points on the surface. Using these points, the CMM tells us whether a part is within tolerance or not.
CMMs are widely used in manufacturing and quality control because they provide high accuracy, repeatable results, and reliable inspection of complex parts.
Probes
CMM probes convert physical measurements into electrical signals, which are then processed by the Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) to determine accurate coordinates.
CMM probes are available in a wide range of designs and are used for both direct measurement and comparative measurement applications.
CMM probes are broadly classified into three main types:
1. Touch-Trigger Probes
Touch-trigger probes are the most commonly used CMM probes.
The probe physically touches the surface of the workpiece
Upon contact, an electrical signal is generated
The CMM records the XYZ coordinates of the contact point
The probe then retracts and moves to the next measurement location
This process is repeated point by point. Touch-trigger probes are ideal for:
Discrete point measurement
Prismatic components
General inspection work
2. Displacement Measuring CMM Probes (Scanning Probes)
Displacement measuring probes are also known as scanning probes.
In this method:
The probe is moved continuously over the surface
It remains within its working range
A continuous stream of measurement data is transmitted to the CMM
Scanning contact probes commonly use:
LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer)
Optoelectronic position-sensing systems
These probes are suitable for:
Free-form surfaces
Profile measurement
High-density data collection
3. Proximity or Non-Contact Probes
Proximity or non-contact probes work on a principle similar to scanning probes, but without physical contact with the workpiece.
Instead of LVDTs, they use:
Laser sensors
Capacitive sensors
Video or optical measurement systems
Non-contact probes are preferred for:
Soft or delicate materials
Highly finished surfaces
High-speed inspection requirements
Types of CMM Machines
There are four basic types of stationary CMMs:
Bridge Type CMM
Most widely used
High accuracy and rigidity
Cantilever Type CMM
Open structure for easy loading
Suitable for small to medium parts
Horizontal Arm CMM
Used for large sheet-metal and automotive body inspection
Gantry Type CMM
Designed for very large and heavy components
Common in aerospace and heavy industries
Mechanical Engineering Courses That Industry Actually Uses
Learn Tools of Design & CAD, Analysis & Simulation, Automation & Robotics, and Industry 4.0 used in modern factories.
Join 40+ Mech Courses like GD&T, Siemens NX, SolidWorks, CATIA V5, AutoCAD, ANSYS (FEA & Fluent), ABAQUS, Creo, Fusion 360, CNC Programming, Digital Twins, Python for Mechanical, and Industry 4.0.
Our Courses
Complete Course Library
Access to 40+ courses covering various fields like Design, Simulation, Quality, Manufacturing, Robotics, and more.