Digital Vernier Caliper
Dec 13, 2025
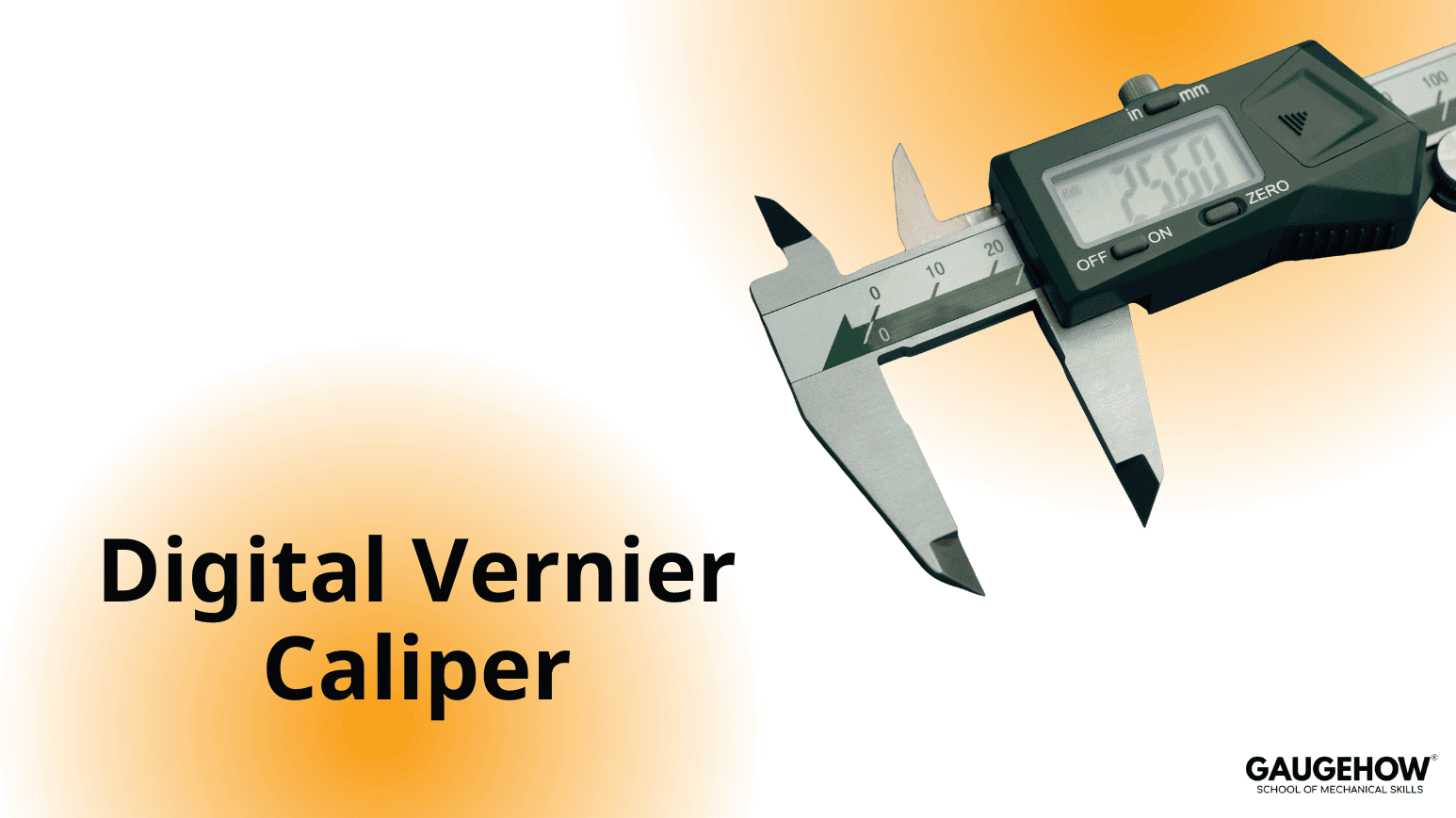
A digital vernier caliper is an upgraded version of the analog vernier caliper. It is a widely used linear measuring instrument with a least count of 0.01 mm, making it more accurate than the analog type.
A digital vernier caliper works on the same measurement principle as an analog vernier caliper, but the measurement is displayed in a digital format, which is faster, clearer, and more convenient.
Construction
A digital vernier caliper consists of:
A main scale
A digital display unit that slides along the main scale
Types of Measurement
Two main types of measurements can be performed:
External measurement – using the external jaws (for shafts, rods, and outer dimensions)
Internal measurement – using the internal jaws (for holes and slots)
The external jaws are divided into three contact surfaces: top, middle, and bottom, allowing better contact depending on the shape and position of the workpiece.
A depth bar is also provided for depth measurement.
Zero Setting
Before taking any measurement, ensure the caliper is set to zero using the zero-setting switch to eliminate zero error.
Material
Digital vernier calipers are typically made of stainless steel or tool steel, depending on the application and required durability.
Advantages
Higher accuracy and better readability
Faster measurements with reduced human error
Reliable and easy to use
Lower maintenance compared to analog vernier calipers
Limitation
More expensive than analog vernier calipers
Digital vernier calipers are preferred where speed, accuracy, and ease of reading are critical.
Mechanical Engineering Courses That Industry Actually Uses
Learn Tools of Design & CAD, Analysis & Simulation, Automation & Robotics, and Industry 4.0 used in modern factories.
Join 40+ Mech Courses like GD&T, Siemens NX, SolidWorks, CATIA V5, AutoCAD, ANSYS (FEA & Fluent), ABAQUS, Creo, Fusion 360, CNC Programming, Digital Twins, Python for Mechanical, and Industry 4.0.
Our Courses
Complete Course Library
Access to 40+ courses covering various fields like Design, Simulation, Quality, Manufacturing, Robotics, and more.




