Common Thermodynamics Interview Questions
Jan 18, 2026


Deepak S Choudhary
🔧 Trusted by 23,000+ Happy Learners
Industry-Ready Skills for Mechanical Engineers
Upskill with 40+ courses in Design/CAD, Simulation, FEA/CFD, Manufacturing, Robotics & Industry 4.0.
Thermodynamics Questions & Answers explains how energy moves as heat and work, and why engines, power plants, and refrigerators have hard limits. It covers system vs control volume, thermodynamic boundary, the laws of thermodynamics, entropy and enthalpy, Carnot efficiency, Otto and Diesel cycles, Rankine and ORC, COP, and A/C refrigeration basics.
Thermodynamics is the study of energy conversion, meaning how heat, work, and stored energy interact in real systems. It helps you predict what is possible, what is waste, and what must be rejected.
Have you ever wondered why an engine cannot turn all heat into useful work, or why a refrigerator needs power even though it only “moves heat”?
This guide answers the most searched Thermodynamics questions in a clean, interview-ready format, covering fundamentals, the laws, core properties like entropy and enthalpy, common cycles, and the practical logic behind COP and refrigeration.
Foundations
Q1) What Is Thermodynamics?
Thermodynamics is the framework for tracking energy and its limits. It tells you how heat and work cross a boundary, how stored energy changes inside, and why every real conversion has losses.
Q2) What Is A Thermodynamic System?
A system is the portion of matter or space you choose to study. Everything outside it is the surroundings, and the separating line is the boundary, real or imaginary.
Q3) What Is A Control Volume In Thermodynamics?
A control volume is an open system where mass can cross the boundary.
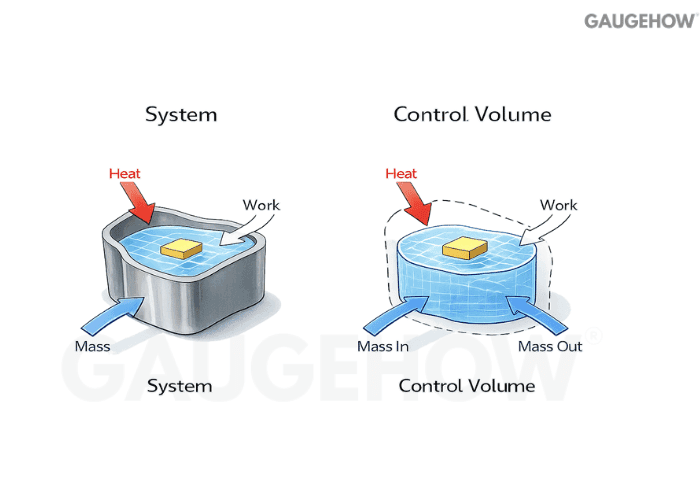
Compressors, turbines, nozzles, and heat exchangers are usually modeled this way.
Q4) What Is The Difference Between Closed, Open, And Isolated Systems?
Closed systems keep mass fixed, but energy can cross the boundary. Open systems allow mass and energy to cross. Isolated systems ideally allow neither.
Closed system: piston–cylinder with no mass leakage
Open system: turbine, compressor, pump, heat exchanger flow path
Isolated system: ideal “no heat, no work, no mass” assumption
That classification matters because it decides whether mass-flow terms belong in your balance.
Q5) What Is The Difference Between A Property, State, Process, And Cycle?
A property is a measurable characteristic like pressure or temperature. A state is a condition defined by properties, a process is the path between states, and a cycle returns to the starting state.
Q6) What Is A Thermodynamic Boundary?
A thermodynamic boundary separates the system from its surroundings. It can be fixed or moving, real or imaginary, and it controls where heat, work, and mass are counted as crossing.
Q7) What Is Energy Transformation?
Energy transformation is a change of form within a system, such as chemical to thermal in combustion or electrical to mechanical in a motor. Total energy stays conserved, but the useful form can shrink.
Q8) What Is Energy Transfer?
Energy transfer is energy crossing a system boundary as heat or work, or carried with mass flow in a control volume. Transfer is about crossing the boundary, not what happens internally.
Q9) What Is Heat In Thermodynamics?
Heat is energy transfer driven by a temperature difference. It is not stored as “heat” inside a body; it exists only while crossing a boundary.
Q10) Heat Vs Work: What Is The Core Difference?
Heat crosses a boundary because of a temperature difference. Work crosses a boundary because a generalized force acts through a displacement.
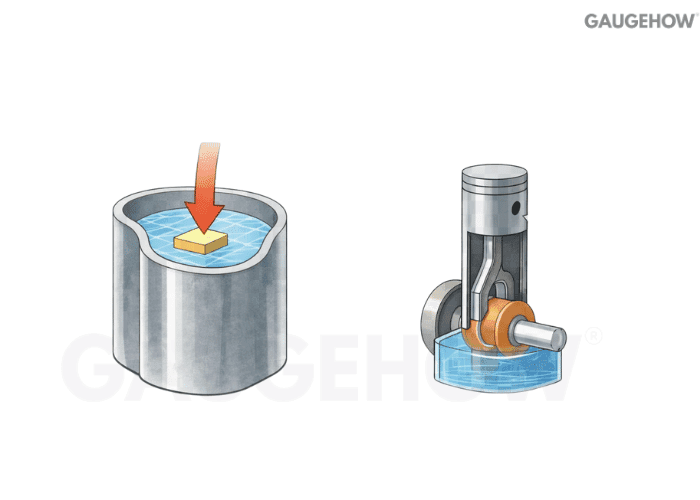
Heat transfer is temperature-driven; work transfer is force-displacement driven.
Heat flowsfrom hot to cold naturally; work needs a mechanism
You can store internal energy, but you cannot “store heat.”
Keeping this clean prevents sign mistakes and broken first-law balances.
Q11) What Is Internal Energy (U) In Simple Terms?
Internal energy is the energy stored microscopically in a system, including molecular motion and bonding effects. In most problems,s you track changes in U, not an absolute zero level.
Q12) What Is Enthalpy (H) And Why Do Engineers Use It?
Enthalpy is defined as
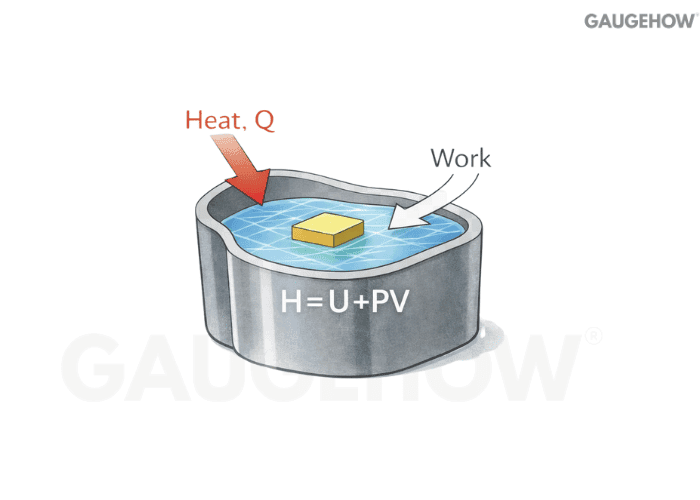
It is convenient for flowing devices because it packages internal energy plus the pressure–volume flow-work term into one property.
Laws & Core Properties
Q13) How Many Laws Of Thermodynamics Are There?
Four are commonly used in engineering: Zeroth, First, Second, and Third laws. People sometimes say “three laws” when they skip the Zeroth, but the standard set is four.
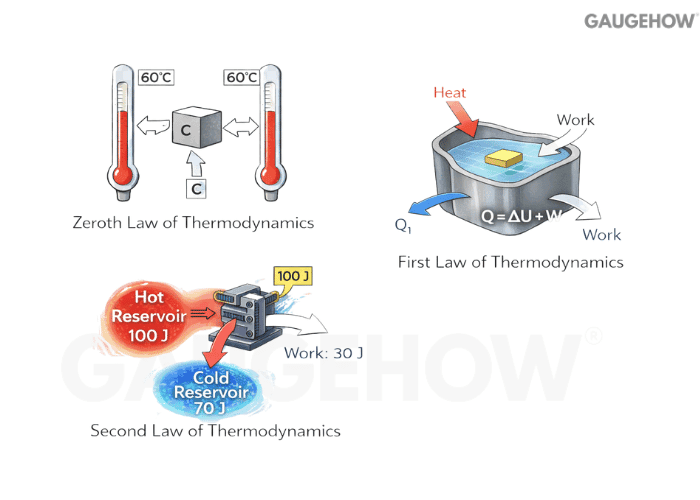
Q14) What Is The First Law Of Thermodynamics?
The first law is energy conservation, meaning energy is neither created nor destroyed. In practice,ce you write an energy balance where heat in minus work out equals the change in stored energy, plus any flow terms for a control volume.
Q15) What Is The Second Law Of Thermodynamics?
The second law adds direction: real processes create entropy, and you cannot fully convert heat into work in a cyclic device without rejecting some heat. It is the reason efficiency has a hard ceiling.
Q16) Can’t We Get 100% Thermal Efficiency From A Heat Engine?
A heat engine must reject some heat to a lower-temperature sink to complete a cycle. If you try to reject nothing, the cycle violates the second law and cannot run.
Q17) What Is The Third Law Of Thermodynamics?
The third law states that as the temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches a minimum constant. Practically, it explains why absolute zero cannot be reached by a finite sequence of steps.
Q18) What Does “Irreversibility” Mean In Real Equipment?
Irreversibility means you cannot restore both the system and the surroundings to the original state without leaving a net change. Friction, throttling, mixing, and heat transfer across a finite temperature difference are common sources, and they destroy available work potential even though total energy is still conserved.
Q19) What Is The Difference Between Enthalpy And Entropy?
Enthalpy tracks energy content in a flow-friendly way. Entropy tracks energy quality and dispersion, so it signals how much useful work potential has been lost to irreversibility.
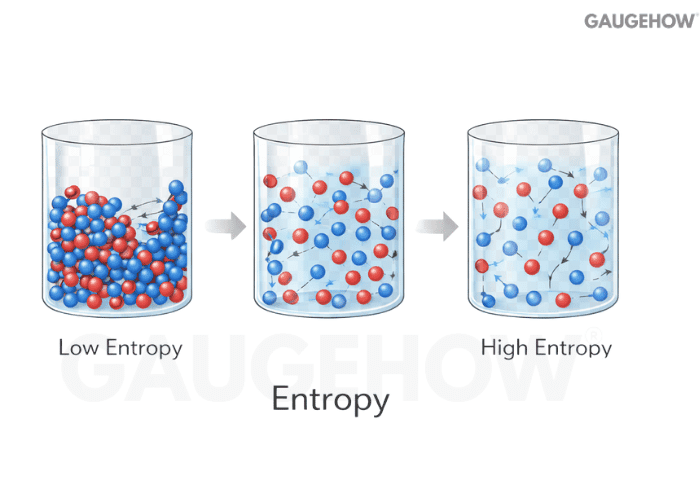
Enthalpy helps with energy balance in devices
Entropy helps with feasibility and performance limits
High entropy generation usually means avoidable losses
Used together, they tell you both the balance and the penalty.
Q20) How Are Enthalpy, Entropy, And Gibbs Free Energy Related?
Gibbs free energy is
At constant temperature and pressure, a decrease in (G) indicates a process can be spontaneous, which is why it is widely used for reactions and phase-change feasibility.
Cycles & Efficiency
Q21) What Is A Heat Engine?
A heat engine takes heat from a high-temperature source, produces net work, and rejects remaining heat to a low-temperature sink. Thermal efficiency is the ratio of net work to heat input.
Q22) What Is Carnot Efficiency And Why Is It A Benchmark?
Carnot efficiency is the maximum possible efficiency for a heat engine operating between two temperature reservoirs. It is a physics limit, not a design claim.
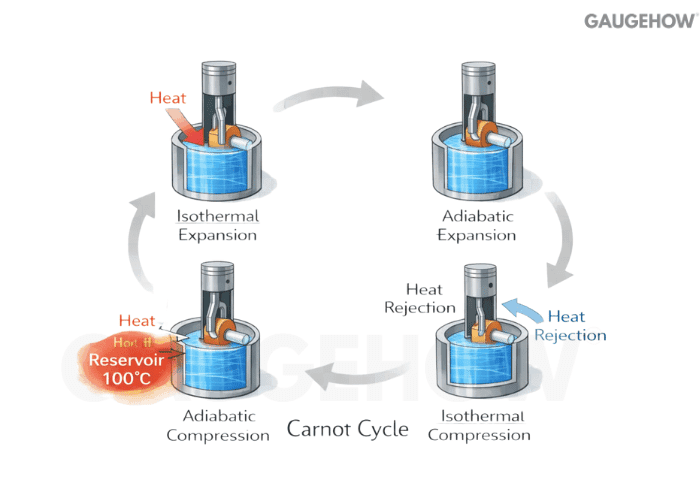
It depends only on TH and TL in absolute units
Raising or TH lowering TL raises the ceiling
Real cycles sit below it due to irreversibility and constraints
That is why Carnot is the first “sanity bound” on any efficiency number.
Q23) How Do You Calculate Carnot Efficiency Quickly?
Use absolute temperatures:
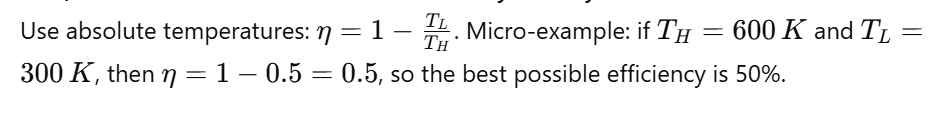
Q24) What Is The Otto Cycle?
The Otto cycle is the idealized cycle for spark-ignition engines. It models compression and expansion as isentropic processes, with heat addition and rejection at constant volume.
Q25) What Is The Diesel Cycle?
The Diesel cycle is the idealized cycle for compression-ignition engines. It models heat addition at constant pressure, which changes the pressure history compared to the Otto model.
Q26) Otto Vs Diesel Cycle: What Actually Changes And Why?
The key difference is the idealized heat-addition process: constant volume for Otto v.s constant pressure for Diesel.
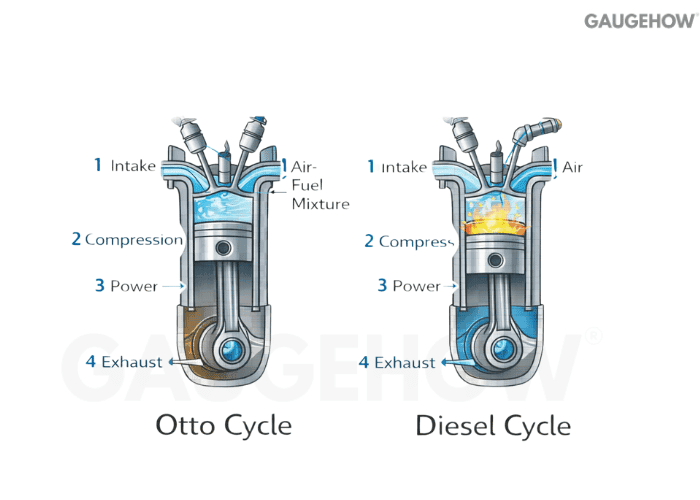
That shift changes peak pressure behavior and efficiency trends with compression ratio, and it maps to how each engine class actually burns fuel.
Q27) What Is The Rankine Cycle?
The Rankine cycle is the base cycle for steam power plants.
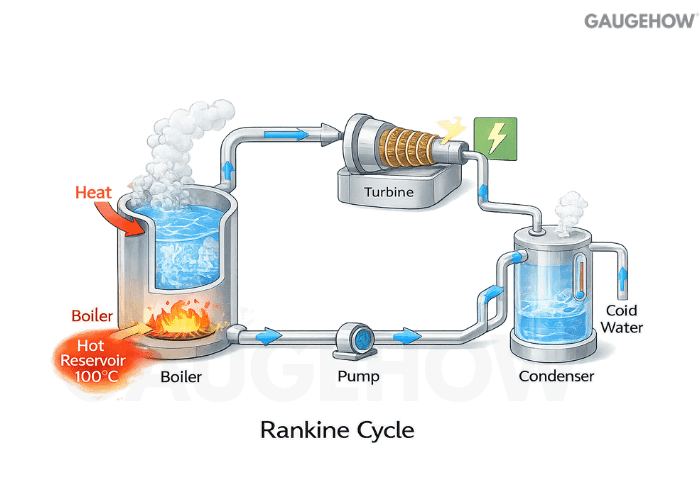
It uses the phase change of water to move large heat rates through the boiler, turbine, condenser, and pump efficiently.
Q28) How Does The Rankine Cycle Work Step By Step?
Pressurized liquid is heated in a boiler to steam, expanded through a turbine to produce work, condensed back to liquid, then pumped to boiler pressure. Each component controls where heat enters, where work exits, and where heat is rejected.
Q29) How Can We Increase Rankine Cycle Efficiency In Practice?
Efficiency improves by raising the average temperature of heat addition and reducing avoidable losses.
Superheat and reheat raise expansion quality and average heat-add temperature.
Regeneration preheats feedwater, reducing low-temperature heat addition
Lower condenser pressure improves turbine work, within practical limits
The design goal is better efficiency without crossing moisture and material limits.
Q30) What Is An Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC)?
An ORC is a Rankine cycle that uses an organic working fluid instead of water. It is used for lower-temperature heat sources such as waste heat recovery and some geothermal applications.
Q31) How Does the Organic Rankine Cycle Work Compared to the Steam Rankine?
The component layout is similar, but the fluid changes operating pressures, turbine sizing, and heat exchanger pinch behavior. ORC becomes attractive when the steam runs too low-pressure or too wet for practical expansion.
Q32) Why Is Working Fluid Selection So Important In ORC?
Fluid choice sets boiling temperature, vapor density, thermal stability, and expansion behavior. A good match improves heat exchanger effectiveness and keeps the turbine and condenser within realistic size and pressure limits.
Refrigeration, COP & Energy Conversion
Device Map:
Heat engine: QH → W + QL
Refrigerator: W + QL → QH
Heat pump: W + QL → QH (same physics, heating intent)
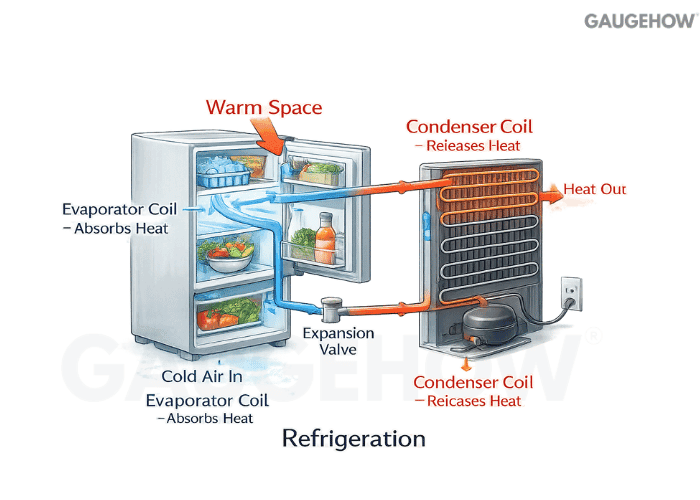
Q33) What Does Refrigeration Mean In Thermodynamics?
Refrigeration is forced heat transfer from a low-temperature region to a higher-temperature region. Power input is required because natural heat flow runs the opposite way.
Q34) What Methods Do Fridges Use To Cool?
Most refrigerators and air conditioners use the vapor-compression cycle.
Vapor compression: compressor, condenser, expansion device, evaporator
Absorption: heat-driven option where waste heat is available
Thermoelectric: compact and quiet, but typically low efficiency
Method choice is an efficiency and application decision, not just a component list.
Q35) How Does Refrigerant Work?
A refrigerant carries heat by changing phase at useful pressures and temperatures. Evaporation absorbs heat at low temperature in the evaporator, then condensation rejects heat at a higher temperature in the condenser.
Q36) What Happens When A Refrigerant Is Compressed And Condensed?
Compression raises pressure and temperature so the refrigerant can reject heat to the surroundings. Condensation then turns vapor into liquid while dumping a large amount of latent heat.
Q37) What Happens During Expansion In Refrigeration?
Expansion drops pressure sharply, which drops saturation temperature and produces a cold mixture feeding the evaporator.
Pressure drop sets the low-temperature level.
Flashing creates a cold liquid–vapor mix.
The evaporator then absorbs QL at that low saturation temperature
This step is intentionally “lossy,” but it is how the cycle creates cooling.
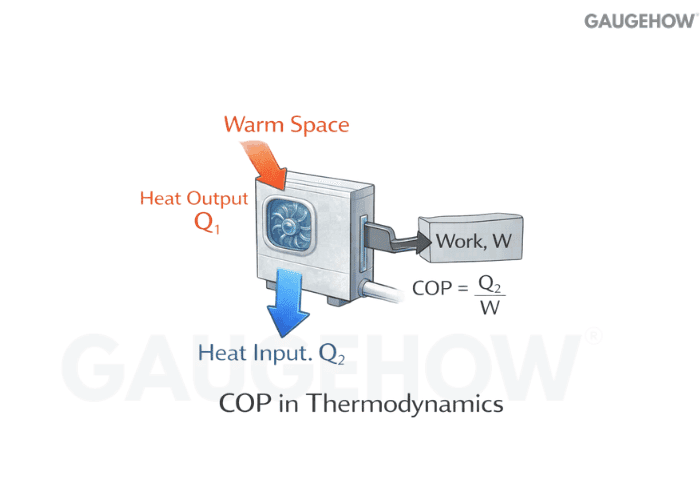
Q38) What Is COP In Thermodynamics, And How Do You Calculate It?
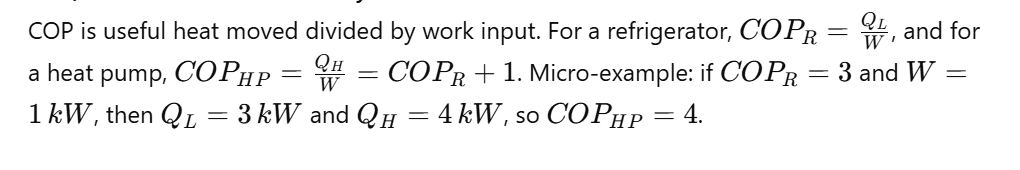
Q39) A/C System Diagram: What Are The Main Components And Flow Path?
A basic vapor-compression A/C loop is:
Evaporator (absorbs QL) → Compressor (adds W) → Condenser (rejects QH)
→ Expansion valve/capillary (drops pressure) → back to Evaporator
That same loop can act as a heat pump if you reverse which coil is indoors.
Q40) When Should Refrigerant Be Removed From The Condenser Outlet?
Remove refrigerant only during controlled recovery or service procedures, after the system is isolated and stabilized per the manufacturer’s service method. In practical terms, recovery is done using proper recovery equipment and compliance steps, and refrigerant should never be vented to the atmosphere.
Conclusion
Thermodynamics is not about memorizing formulas. It is about choosing the right boundary, tracking heat and work cleanly, and respecting the second law when you judge what efficiency can mean.
Once you separate energy transfer from energy transformation, most mistakes become obvious. Next, practice by sketching a control volume, listing Q, W, and mass flows, then checking entropy generation. That routine makes engines, Rankine plants, and refrigeration cycles predictable and design-ready, even when conditions and hardware change.
